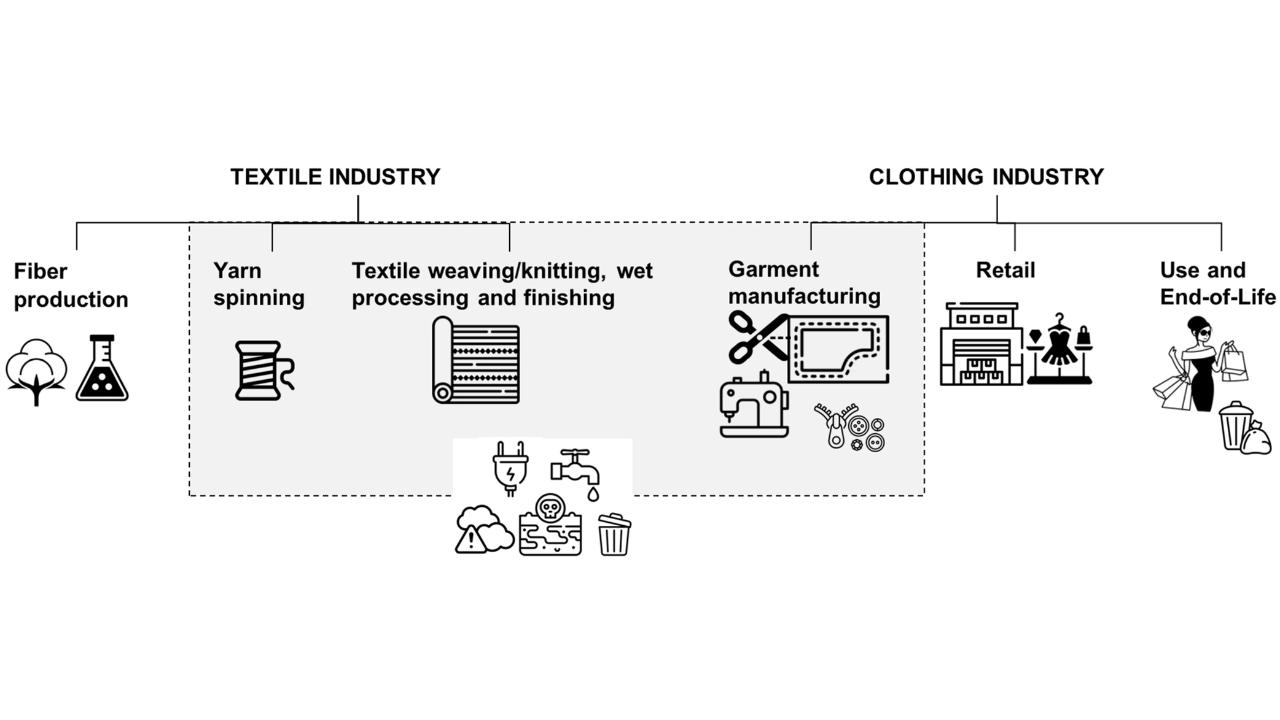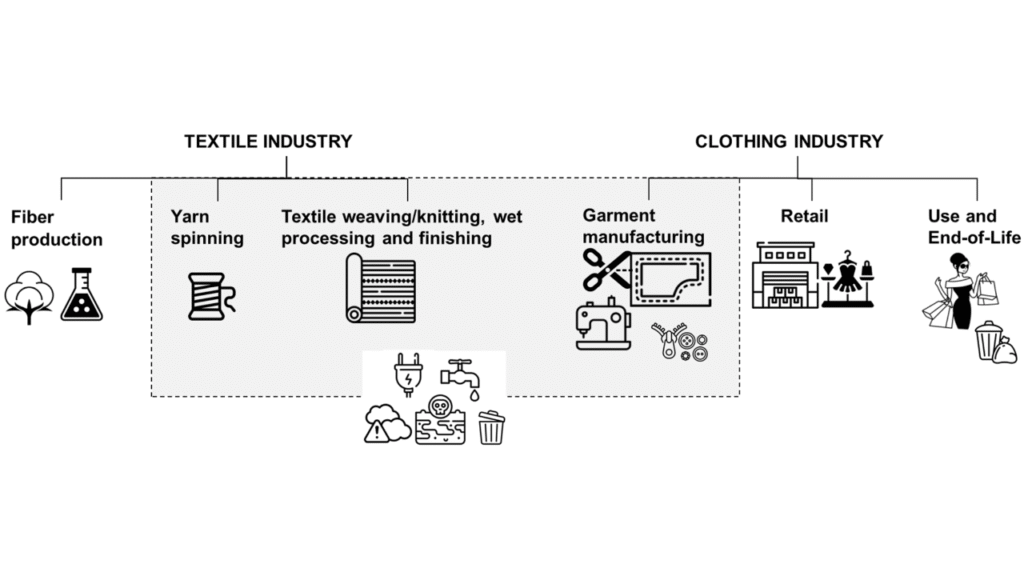
A renewed focus on supply-chain modernization now shapes the textile sector in Costa Rica as manufacturers seek greater efficiency, resilience, and ecological responsibility. A strategic shift toward sustainability encourages the adoption of cleaner processes, local sourcing, and advanced value-addition techniques that strengthen competitiveness. A forward-looking approach drives factories to rethink procurement, production flow, and product differentiation in ways that reflect global expectations and national priorities.
Sustainability as a Core Supply-Chain Priority
A rising environmental consciousness influences how textile companies manage raw materials, energy consumption, and waste streams.
- Commitment to reducing water usage through low-liquor dyeing systems
- Incorporation of renewable energy sources into production operations
- Reduction of chemical discharge by shifting to certified eco-friendly dyes
- Introduction of circular-economy programs promoting fabric reuse
- Alignment with international sustainability certifications
A deeper sustainability mindset transforms supply chains from linear systems to regenerative models that emphasize long-term resource stewardship.
Local Input Development Strengthening Supply Chains
A growing interest in domestic sourcing helps manufacturers reduce dependency on imported materials and external supply disruptions.
- Procurement of locally grown natural fibers, where available
- Development of relationships with national yarn processing units
- Use of regional accessory suppliers for trims, labels, and buttons
- Faster replenishment cycles due to shorter transportation distances
- Lower carbon footprint compared to long-distance imports
A demand for supply-chain resilience motivates companies to invest in long-term partnerships with Costa Rican producers to stabilize quality and improve predictability.
Key Advantages of Using Local Inputs
Local Sourcing Benefits
| Category | Benefit Description |
|---|---|
| Lead Times | Substantially shorter ordering cycles compared to overseas sourcing |
| Quality Control | Easier inspection of materials and supplier processes |
| Environmental Impact | Lower emissions due to reduced transport requirements |
| Economic Contribution | Stronger support for regional small and mid-size businesses |
| Supply Stability | Less vulnerability to port delays or international logistics disruptions |
Innovation in Fabric Treatments and Finishing
A wave of technical innovation moves the textile sector toward higher-value niche products.
- Development of anti-microbial fabrics for domestic and export markets
- Use of laser finishing for precision texturing and fabric personalization
- Application of moisture-management coatings for sports and outdoor wear
- Introduction of UV-resistant treatments for specialized garments
- Experimentation with biodegradable finishing agents
A shift toward performance textiles enhances the industry’s ability to compete in segments that require innovation rather than high-volume, low-cost production.
Integration of Smart Logistics and Digital Workflow Systems
A digital transformation trend changes how textile supply chains track materials, schedule production, and coordinate shipping.
- Adoption of cloud-based supply-chain management systems
- Use of barcoding and RFID tagging for fabric roll traceability
- Real-time monitoring of production stages through integrated dashboards
- Automation of inventory control to reduce human error
- Electronic coordination with suppliers and buyers to minimize delays
A data-driven culture enables manufacturers to predict shortages, optimize capacity, and maintain consistent delivery performance.
Digital Tools Transforming Textile Supply Chains
Technology Applications
| Tool | Impact on Operations |
|---|---|
| RFID Tracking | Transparent visibility for every fabric roll in transit |
| AI-Based Forecasting | Improved demand planning and fewer stockouts |
| Cloud SCM Systems | Centralized coordination across suppliers and production units |
| Automated Cutting Systems | Higher precision and reduced fabric waste |
| Quality Scanning Devices | Faster detection of defects during production |
Value Addition Through Design and Specialized Production
A creative expansion in capabilities drives interest in producing smaller, high-quality, differentiated batches.
- Development of artisanal textile lines that highlight Costa Rican craftsmanship
- Incorporation of digital printing for custom designs
- Production of eco-friendly fashion capsules using recycled fibers
- Manufacturing of uniforms and technical gear with tailored specifications
- Emphasis on design-led production rather than mass manufacturing
A growing design ecosystem supports value-addition by linking creative professionals with textile engineers and material specialists.
Sustainable Packaging Innovations
A shift in packaging practices ensures that sustainability carries through to finished goods.
- Use of compostable or biodegradable garment bags
- Replacement of traditional plastic with recycled paper-based materials
- Adoption of compact folding techniques that reduce packaging volume
- Introduction of minimal-ink labeling to lower environmental impact
- Partnerships with local packaging innovators focused on eco-friendly solutions
Collaborative Networks Supporting Innovation
A collaborative environment emerges as industry associations, research institutions, and manufacturers work together to strengthen supply chains.
- Joint research projects focused on alternative fibers
- Collaborative sourcing agreements among smaller factories
- Shared logistics solutions to reduce transport costs
- Partnerships with universities for testing new materials
- National programs that support green entrepreneurship in textiles
A cooperative approach ensures that innovation spreads beyond large manufacturers and reaches the broader industry.
Sustainability Metrics Guiding Supply-Chain Decisions
A performance-driven framework helps companies measure the impact of their sustainability efforts.
- Tracking of water consumption per production batch
- Calculation of carbon emissions for each supply-chain step
- Assessment of chemical usage intensity in dyeing and finishing
- Monitoring of waste reduction improvements over time
- Evaluation of recyclability rates for fabric scraps and packaging
Economic Benefits of Supply-Chain Innovation
A clear economic upside follows companies that adopt innovative supply-chain practices.
- Higher efficiency reduces costs across production stages
- Stronger market positioning attracts international buyers
- Sustainable branding enhances consumer trust
- Better stock control lowers waste and overproduction
- Improved reliability strengthens long-term contracts
In Summary
A transformative movement in Costa Rica’s textile supply chain integrates sustainability, local input development, and innovation-driven value addition. A modernized network of suppliers, designers, and manufacturers now collaborates to create efficient, environmentally responsible systems that support long-term growth. A progressive outlook positions the industry for stronger global competitiveness through cleaner processes, smarter technology, and creative product differentiation.